As you already probably know, it isn’t easy to provide a complete balance of nutrients to plants in a lawn care setting. Treating many lawns with varying nutrient deficiencies leads the process to be time-consuming and expensive.
To help get over this hurdle, we brought Armament technology to the market. It bridges many gaps in imbalances and nutrient tie-ups in the soil. It’s not the end-all and be-all for managing nutrient issues, but it does make up for a lot.
So, why Armament? Compromised soils. There are significant hurdles to overcome in compromised soils regarding nutrient availability, and Armament tackles them. Armament is effective in high pH, low pH, high phosphorus, high bicarbonate, high clay content, low CEC, and low organic matter soils. These are all situations where nutrients are tied up or unavailable and where Armament has been very successful at freeing up these nutrients for better plant uptake.
Let’s expand upon these compromised soils. Several chemical interactions in compromised soils render nutrients unavailable for plant use. Here are just a few examples: calcium phosphate, magnesium bicarbonate, magnesium phosphate, and iron oxide. These are all very insoluble forms of the nutrients, meaning they won’t stay in solution so the plant can use them. Armament inhibits these interactions, so nutrients remain available for plant uptake.
Demonstrating the Effectiveness of Armament Technology in Compromised Soils
Here are the results of a leaf tissue test from a turf grass sample taken from a putting green on a golf course near Cincinnati, Ohio.
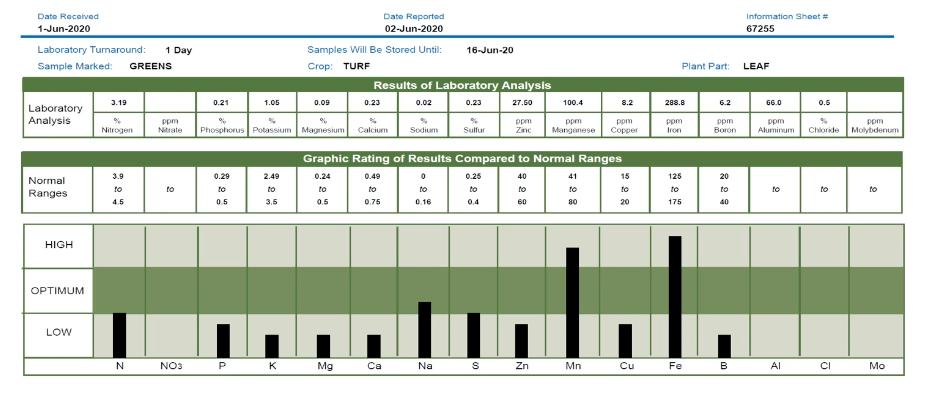
As you can see, many of the nutrient values are below optimum. The day after this tissue sample was taken, the Superintendent applied Armament K and Armament P and watered them in. Then, five days after that application, another leaf tissue sample was taken and sent in for analysis.
Now, let’s compare the two tissue samples, one from before the Armament P and Armament K application and one after the application.
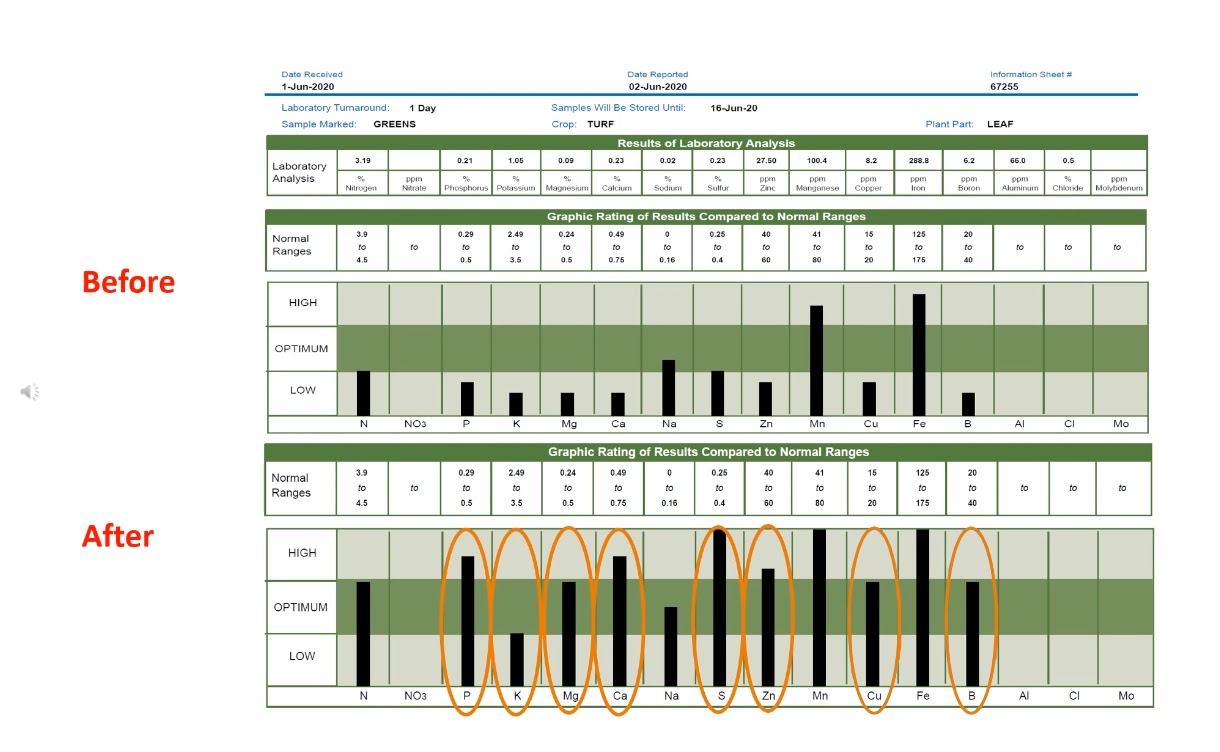
Not only did the phosphorous and the potassium increase in the test after the application, but we also received a bump up of magnesium, calcium, sulfur, zinc, copper, and boron.